Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing: What’s the Future?
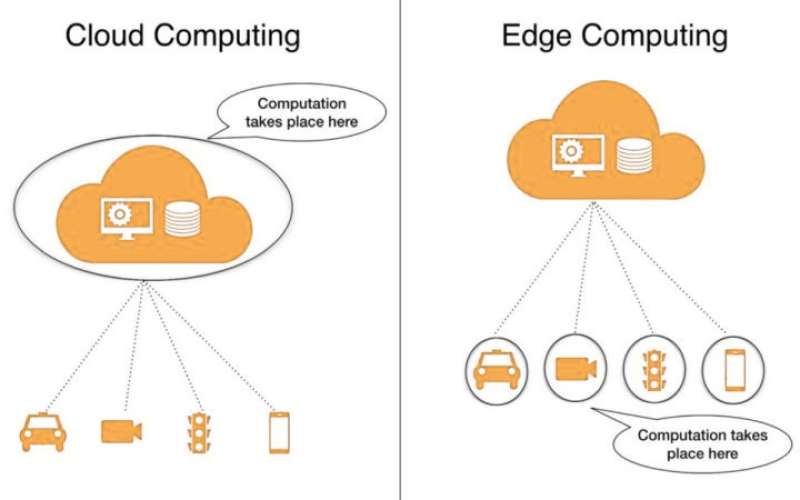
Edge computing enables real-time processing at the source, while cloud computing provides scalability. The future lies in a hybrid approach.
Introduction
As digital transformation accelerates, businesses and developers are exploring new computing paradigms to handle massive data loads efficiently. Two major approaches, Edge Computing and Cloud Computing, offer unique advantages and challenges. Understanding their differences, benefits, and future trends is crucial for making informed technology decisions.
What is Edge Computing?
Edge computing is a decentralized computing model that processes data closer to the source rather than relying on a distant data center. This reduces latency and improves real-time decision-making, making it ideal for IoT (Internet of Things) devices, smart sensors, and autonomous systems.
Key advantages of edge computing include:
✅ Low Latency – Data processing happens near the device, reducing delays.
✅ Bandwidth Efficiency – Less data is transmitted to the cloud, reducing network congestion.
✅ Enhanced Security – Sensitive data is processed locally, reducing exposure to cyber threats.
✅ Offline Capabilities – Edge devices can continue functioning even with limited internet connectivity.
Common use cases: Smart homes, industrial automation, autonomous vehicles, healthcare monitoring, and gaming.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services such as storage, processing power, and software applications over the internet. Public cloud providers like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer scalable, on-demand resources that businesses can leverage without maintaining physical infrastructure.
Key advantages of cloud computing:
✅ Scalability – Resources can be scaled up or down based on demand.
✅ Cost Efficiency – Pay-as-you-go pricing eliminates upfront hardware investments.
✅ Global Accessibility – Users can access data and applications from anywhere.
✅ High Computational Power – Suitable for AI/ML training, big data processing, and SaaS applications.
Common use cases: Enterprise applications, data analytics, AI model training, online collaboration tools, and media streaming.
Key Differences: Edge Computing vs. Cloud Computing
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Latency | Low (near-instant processing) | Higher due to remote processing |
| Data Processing Location | At the edge (device/source) | Centralized in cloud servers |
| Security | Enhanced (localized data processing) | Vulnerable to cyber-attacks |
| Scalability | Limited by hardware | Virtually unlimited |
| Use Cases | IoT, real-time analytics, gaming | AI, SaaS, enterprise software |
What’s the Future of Computing?
Neither edge computing nor cloud computing will replace the other entirely. Instead, the future lies in a hybrid approach that combines the strengths of both:
🔹 Hybrid Cloud-Edge Models – Companies will use edge computing for real-time decision-making and cloud computing for large-scale data storage and processing.
🔹 5G & Edge Synergy – Faster networks will boost the capabilities of edge devices, making smart cities and autonomous vehicles more efficient.
🔹 AI & Edge Computing – More AI models will run on edge devices, reducing the need for cloud-based inference.
🔹 Security Enhancements – Edge computing will play a key role in cybersecurity by enabling real-time threat detection.
Conclusion
Edge computing and cloud computing are complementary rather than competing technologies. While cloud computing provides scalability and cost efficiency, edge computing enables faster processing, security, and real-time decision-making. The future of computing lies in leveraging both models to optimize performance across industries.
Keywords
Edge computing, cloud computing, edge vs. cloud, real-time data processing, hybrid cloud, future of computing, IoT computing, cloud scalability, AI at the edge, cloud security.



Write A Comment
No Comments